Describe the Orbitals Used by the Carbon Atom in Bonding
A covalent bond forms between the two atoms by the overlap of half-filled valence atomic orbitals from each atom. 2 rows The carbon has three sigma bonds.

What Are Hybrid Orbitals Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Organic Chemistry Books
View chapter Shortcuts Tips.
. A molecule in which s p 2 hybrid orbitals are used by the central atom in forming covalent bond is. A shared electron pair has the highest probability of being located between the nuclei of the bonded atoms. What type of hybrid orbitals form around the carbon.
Tap card to see definition. The bond between carbon and single bonded oxygen atom is formed by hybrid orbital of carbon atom and hybrid orbital of oxygen atom. The triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
Click card to see definition. Reset Help sp sp. View solution View more.
Two double bonds and one lone pair of electrons. In chemistry valence bail VB theory is ane of two basic theoriesalong with molecular orbital MO theorythat employ quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. Predict the geometry of the molecule.
There are three electron groups surrounding the central sulfur atom. Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules. Valence bond theory.
Ethane C2H6 has 24 61 14 valence electrons. Because carbon is s p2 hybridized the bond angles are approximately 120circ. Start by drawing the Lewis diagram for SO2.
It uses its leftover p orbital to form the second bond to oxygen. Science Chemistry QA Library Describe the orbitals used in bonding and the bond angles in the following compounds. While if there is one double bond made by a carbon with other items then the hybrid orbitals involved are sP two.
B the carbon uses s p3 hybridizied orbitals. Because carbon forms a double bond we know that it uses s p2 orbitals as it does in ethene to bond to the two hydrogens and the oxygen. Part F Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond angles.
How many π bonds are there between the carbon and the nitrogen. OH 1095 H 120 180. Describe the orbitals used in bonding and the bond angles in the following compounds.
Click again to see term. Hybrid orbitals from each carbon atom. The space formed by overlapping orbitals can accommodate a maximum of two electrons.
The extent of orbital overlap depends on the shape and direction of the orbitals involved. A Lewis structure of H_2 C O_3 b the carbon uses s p2 hybridized orbitals. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
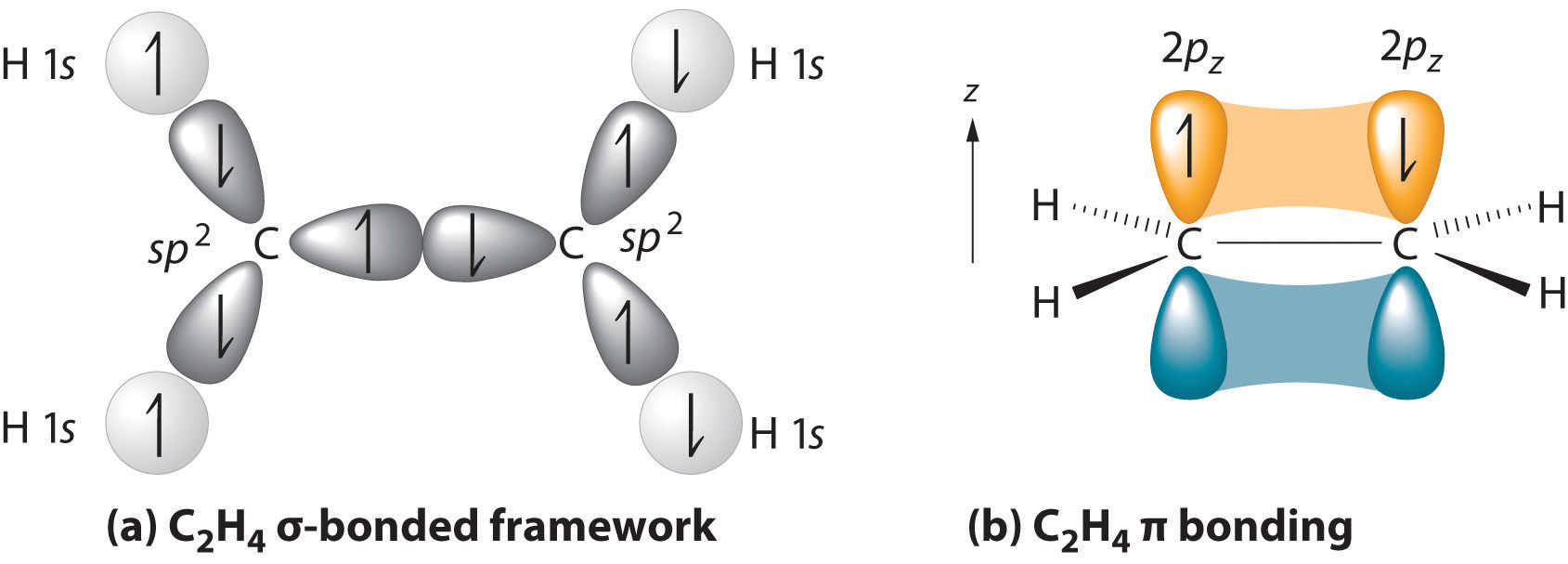
In the ethene molecule C 2 H 4 there are a five σ bonds. SOLUTION TO 31 b. How many unmorphed p-orbitals remain on the carbon atom in this compound.
The two π bonds of the triple bond are formed from parallel overlap of the two unhybridized p atomic orbitals from each carbon. How many σ bonds are there between the carbon and the nitrogen. Therefore the bond angles are 1095circ 4.
The Lewis structure is. Solution for Describe the hybrid orbitals used by the carbon atom inNC-Cl. According to MO theory one sigma orbital is lower in energy than either of the two isolated atomic 1s orbitals this lower sigma orbital is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital.
Therefore the bond angles are close to 120circ. One CC σ bond results from overlap of sp 2 hybrid orbitals on the carbon atom with one sp 2 hybrid orbital on the other carbon atom. These two perpendicular pairs of p orbitals form two pi bonds between the carbons resulting in.
Each carbon atom still has two half-filled 2p y and 2p z orbitals which are perpendicular both to each other and to the line formed by the sigma bonds. Four CH bonds result from the overlap between the C atoms sp 2 orbitals with s orbitals on the hydrogen atoms. Not all labels will be used.
Solution for Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond angles1. 10 Use the structure below to answer the following questions. B The π bond is formed by the side-by-side overlap of the two unhybridized.
Molecular orbitals for H2. Generally the number of. When two atomic 1s orbitals combine in the formation of H2 the result is two sigma σ orbitals.
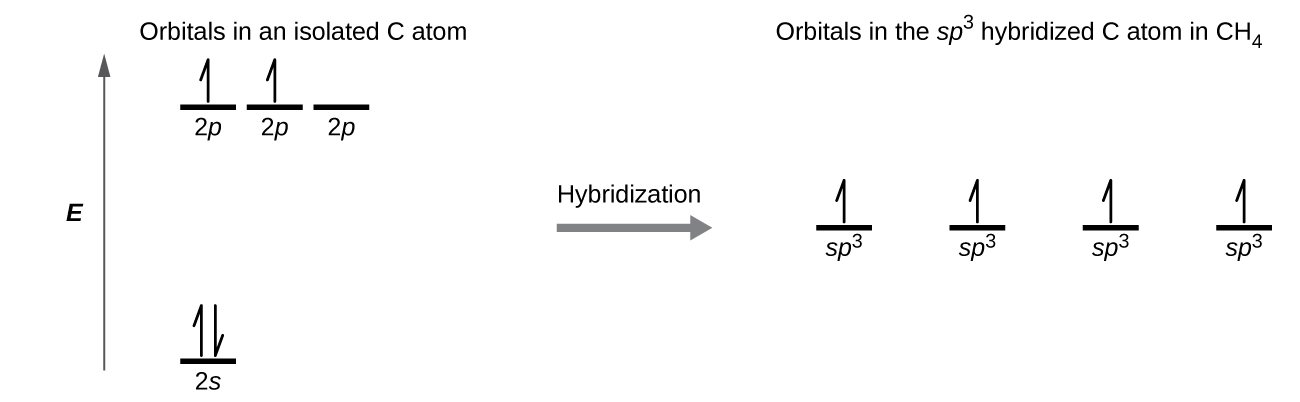
The carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized. No on the basis of the fact that if all single bonds are made by a carbon then it utilizes its sP three hybrid orbital. Ill assume you already know how to do this.
And if one triple bond is made by a carbon atom then the orbitals involved are sp. The pi bond between carbon and double bonded oxygen atom is formed by unhybridized p-orbitals of carbon and oxygen. A C H 3.
The six CH sigma bonds are formed from overlap of. Two are formed by overlap between sp2 orbitals with 1s. 0 8p H H.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure.

What Is An Sp3 Hybridized Carbon Atom A Plus Topper Sp3hybridization Atom Carbon Chemistry

10 7 Multiple Bonding And Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts

2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook

2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook
8 2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Chemistry
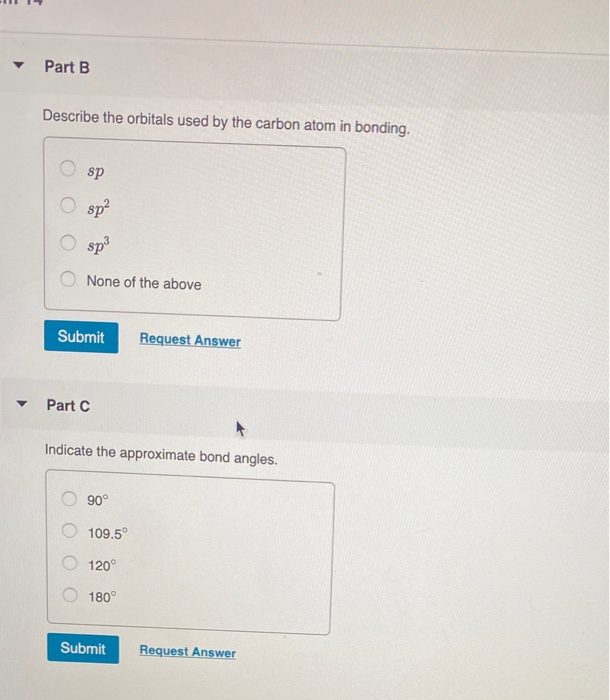
Solved Part B Describe The Orbitals Used By The Carbon Atom Chegg Com
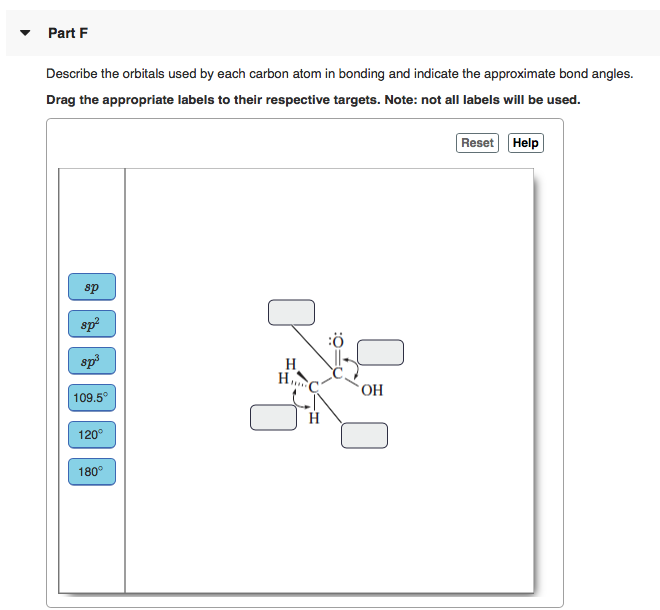
Solved Part F Describe The Orbitals Used By Each Carbon Atom Chegg Com

Hybrid Orbitals Infographic Linus Pauling S Explanation Of Bonding Mechanisms Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry

What Are Hybrid Orbitals Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Chemistry

Hybridization And Hybrid Orbitals Chemistry Notes Covalent Bonding Chemistry Education
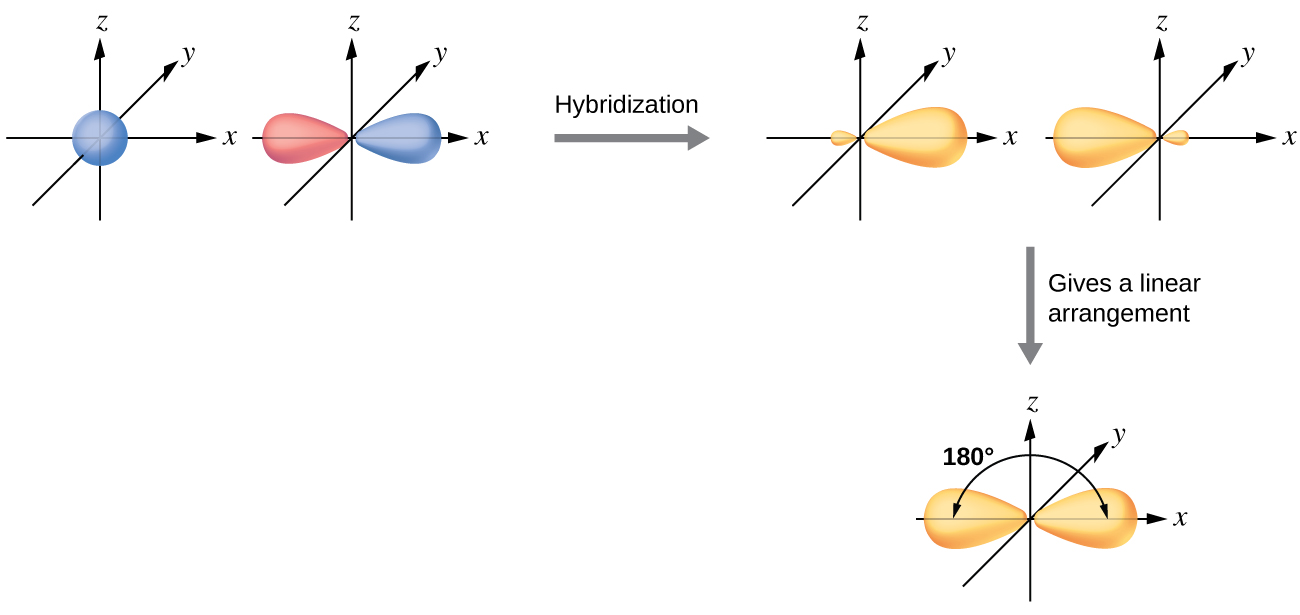
8 2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Chemistry

Ethene Reactions Of Ethene Properties Of Ethene Chemistry Education Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Help

Main Difference Hybrid Orbitals Vs Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Basics Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom
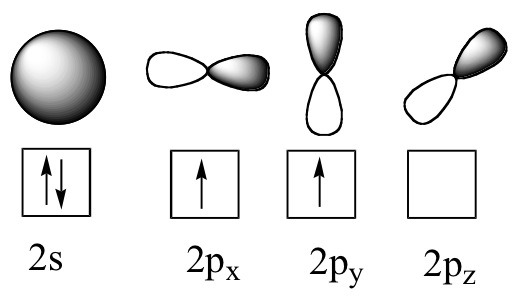
12 3 Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts

What Are Hybrid Orbitals Master Organic Chemistry Chemistry Organic Chemistry College Chemistry

Carbene Covalent Bonding Organic Chemistry Inert Gas

What Are Hybrid Orbitals Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Chemistry Molecular Geometry

1 1 5the Nature Of Chemical Bonds Valence Bond Theory Covalent Bond Forms When Two Atoms Approach Each Other Closely Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Chemistry

Comments
Post a Comment